March 10.
Forty Martyrs of St. Sebasti, A.D. 320. St. Drocovoeus, Abbot, A.D. 580. St. Mackessoge.
The 10th of March, 1702, is erroneously said to have been the day whereon died sir Hugh Myddleton; a man renowned in English annals for having abundantly supplied London with water, by conducting the New River from Ware, in Hertfordshire, to the Clerkenwell suburb of the metropolis.
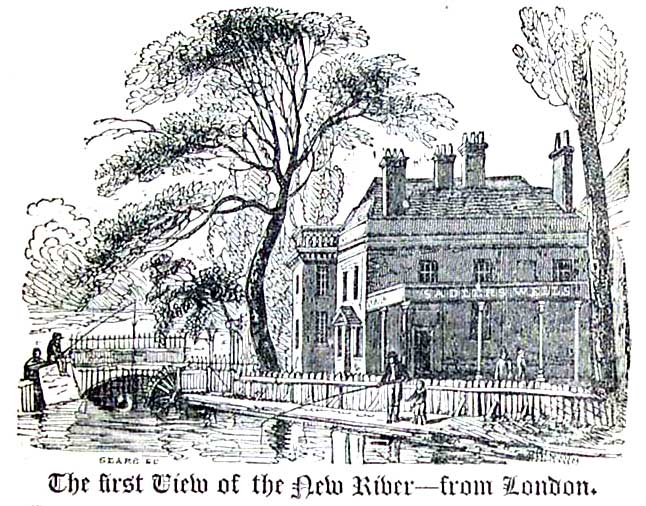
The first View of the New River—from London.
This is seen immediately on coming within view of Sadler's Wells, a place of dramatic entertainment. After manifold windings and tunnellings from its source, the New River passes beneath the arch in the engraving, and forms a basin within a large walled enclosure, from whence diverging main pipes convey the water to all parts of London. At the back of the boy angling on the wall, is a public-house with tea-gardens and a skittle-ground, "commonly called, or known by the name or sign of, the sir Hugh Myddleton, or of the sir Hugh Myddleton's head," a portrait of sir Hugh hangs in front of the house. To this stream, as the water nearest London favourable to sport, anglers of inferior note repair:—
Here "gentle anglers," and their rods withal,
Essaying, do the finny tribe inthrall.
Here boys their penny lines and bloodworms throw,
And scare, and catch, the "silly fish" below:
Backstickles bite, and biting up they come,
And now a minnow, now a miller's thumb.
Here too, experienced youths of better taste
And higher aim resort, who bait with paste,
Or push beneath a gentle's shining skin
The barbed hook, and bury it within;
The more he writhes the better, if he die
Not one will touch him of the finny fry;
If in strong agony the sufferer live,
Then doth the "gentle angler" joy receive,
Down bobs the float, the angler wins the prize,
And now the gentle, not the gudgeon dies.
Concerning Sir Hugh Myddleton there will be occasion to speak again.
GLOVE OF DEFIANCE
In the Church.
In the notice of Bernard Gilpin, March 4, (p. 332,) it is said, "another incident further illustrating the manners of the Northern Borderers will be mentioned below." The observation refers to a singular challenge, which the arrangements of that day could not include, and is now inserted.
On a certain Sunday Mr. Gilpin going to preach in those parts wherein deadly feuds prevailed, observed a glove hanging up on high in the church. He demanded of the sexton what it meant, and why it hung there. The sexton answered, that it was a glove which one of the parish hung up there as a challenge to his enemy, signifying thereby, that he was ready to enter combat hand to hand, with him or any one else who should dare to take the glove down. Mr. Gilpin requested the sexton to take it down. "Not I, sire," replied the sexton, "I dare do no such thing." Then Mr. Gilpin, calling for a long staff, took down the glove himself, and put it in his bosom. By and by, when the people came to church, and Mr. Gilpin in due time went up into the pulpit, he in his sermon reproved the barbarous custom of challenges, and especially the custom which they had, of making challenges by the hanging up of a glove. "I hear," said he, "that there is one amongst you, who, even in this sacred place, hath hanged up a glove to this purpose, and threateneth to enter into combat with whosoever shall take it down. Behold, I have taken it down myself." Then plucking out the glove, he showed it openly, and inveighing against such practices in any man that professed himself a Christian, endeavoured to persuade them to the practice of mutual love and charity.
THE SEASON.
The memory of man supplies no recollection of so wet a season as from September 1824 to March 1825; it produced the rot in sheep to an alarming extent. In consequence of the animals being killed in this disease, the mutton is unwholesome for human food, and produces mortality even in dogs. The newspapers relate that such mutton given to a kennel of dogs rendered them fat, till on a sudden their good looks declined, they became lean, and gradually died, without any other cause being assignable for the mortality, than the impure flesh of the sheep. In such a season, therefore, families should shrink from the use of mutton as from a pestilence. There is no security, but in entire abstinence. Almost every hare shot during the same period had a tainted liver. Under such circumstances lamb should be sparingly used, and, if possible, refrained from altogether, in order to secure mutton at a reasonable price hereafter.
CHRONOLOGY .
1792. John, earl of Bute, died. He was prime minister soon after the accession of George III.; and of all who guided the helm of state, the most unpopular.
On the 10th of March, 1820, died Benjamin West, esq., president of the Royal Academy, in the eighty-second year of his age. It was his delight to gently lead genius in a young artist; and Mr. WILLIAM BEHNES, the sculptor, was honoured by the venerable president with the means of transmitting his parting looks to an admiring world, upon whom he was soon to look no more. Mr. West's sittings to Mr. Behnes were about two months before his death. Expressing himself to his young friend in terms of high satisfaction at the model, he encouraged him to persevere in that branch of art which Mr. Behnes has since distinguished, by admirable power of design and use of the chisel. To speak of Mr. Behnes's model as a mere likeness, is meagre praise of an effort which clearly marks observation, and comprehension, of Mr. West's great mental powers. The bust, as it stands in marble, in sir John Leicester's gallery, is a perfect resemblance of Mr. West's features, and an eloquent memorial of his vigorous and unimpaired intellect in the last days of earthly existence. If ever the noblest traits of humanity were depicted by the hand of art, they are on this bust. Superiority of mind is so decidedly marked, and blended, with primitive simplicity, and a beaming look of humanity and benevolence, that it seems the head of an apostle.
Mr. West was an American; he was born at Springfield, in Pennsylvania, on the 10th of October, 1738; his ancestors and parents were "Friends:" the family had emigrated from England with the illustrious founder and legislator of Pennsylvania, WILLIAM PENN: of whose treaty with the Indians for a tract of their territory, it is observed, that it was the only christian contract unsanctioned by an oath, and the only one never violated.* [1] The first of the family who embraced Quaker principles was colonel James West, the friend and companion in arms of the great John Hampden.
Mr. West's genius developed itself very early. When a child he saw an infant smile in its sleep, and forcibly struck with its beauty, seized pens, ink, and paper, which happened to lie by him, and endeavoured to delineate a portrait; at this period he had never seen an engraving or a picture. He was afterwards sent to school in the neighbourhood, and during hours of leisure was permitted to draw with a pen and ink. It did not occur to any of the family to provide him with better materials, till a party of Indians being amused with little Benjame's sketches of birds and flowers, taught him to prepare the red and yellow colours with which they painted their ornaments, and his mother adding blue, by giving him a piece of indigo, he became possessed of the three primary colours. As he could not procure camels' hair pencils, and did not even know of their existence, he supplied the deficiency by cutting fur from the end of the cat's tail. From the frequent necessity for repeating this depredation, his father observed the altered appearance of his favourite, and lemanted it as the effect of disease; the young artist, with due contrition, informed his father of the true cause, and the old gentleman was highly pleased by his son's ingenuousness. Mr. Pennington, a merchant of Philadelphia, struck with the genius of the child, sent him a box of paints and pencils, with some canvass, and six engravings by Grevling. Little West rose with the dawn of the next day, carried the box into the garret, prepared a pallet, began to imitate the figures in the engravings, omitted to go to school and joined the family at dinner, without mentioning how he had been occupied. In the afternoon he again retired to his garret; and for several successive days thus devoted himself to painting. The schoolmaster, however, sent to know the reason of his absence. Mrs. West recollecting that she had seen Benjamin going up stairs every morning, and suspecting that it was the box which occasioned this neglect of the school, affected not to notice the message but went immediately to the garret, and found him employed on the picture. If she had anger, it was changed to a different feeling by the sight of his performance; she kissed him with transports of affection, and assured him that she would intercede to prevent his being punished. It seemed ever the highest pleasure of Mr. West emphatically to declare, that it was this kiss that made him a painter.
After numerous indications of uncontrollable passion for his favourite and only pursuit, a consultation of "Friends" was held, on the propriety of allowing young West to indulge a taste, which the strict discipline of the society inhibits:—
Genius has such resistless power
That e'en the Quaker, stern and plain,
Felt for the blooming painter boy.The destiny he desired was fixed. In 1760 he left Philadelphia for Rome, pursued his studies in the capital of art, visited the galleries and collections of Italy with an ardour that impaired his health, came through France and London, and was about to return to America, when sir Joshua Reynolds, and Wilson, the landscape painter, used their utmost persuasions to detain him in this country. There was only one abstacle; he had formed an attachment on his native soil:
Wheree'er he turn'd, whatever realms to see,
His heart, untravell'd, fondly turn'dto her whom he loved. This difficulty was overcome, for the lady, Miss Shewell, came over: they were married in London, in 1764. Thus "settled," in the following year Mr. West was chosen a member and one of the directors of the Society of Artists, afterwards incorporated with the Royal Academy, which he assisted in forming, and over which he afterwards presided till his death.
As an artist his works in the various collections and edifices throughout England exhibit his talents, but above all "West's Gallery," now open in Newman-street for public inspection, is an assemblage of testimonials to the justice of his fame among his adopted countrymen. His talent germinated on the shores of the Atlantic, but with us it flourished. America at that period was not sufficiently advanced to cultivate his genius: now that she has risen in commerce and the arts, and taken her stand amont the nations, she will retain her future Wests to adorn her greatness. May the people of England and America contend with each other no more but in works of peace and good will; and may the interchange of talented individuals from each, contribute to the propriety and moral grandeur of both countries!
As a man, Mr. West's characteristics were kindness and warmth of heart. From accordant feelings, he painted with delight and energy some of the most affecting incidents in the New Testament history. His "Christ healing the sick" will be remembered by all who saw it, with reverend solemnity. In his "Christ Rejected," the various bad passions in the malignant spectators and abettors of the outrage; the patient suffering of the great and all-enduring character; the sympathizing feelings of his adherents; and the general accessories, are great lineaments of the designer's power. His "Death on the Pale Horse," and more especially the sketch for that painting, express masterly thought and conception. These are Mr. West's "large" pictures. Some of this smaller ones and his sketches, the beholder studies and lingers over till his limbs and body tire; and he leaves the large assemblage of paintings in "West's Gallery" with a conviction, that no artist has yet fully occupied his place. Perhaps there is only one who would have designed the "Death on the Pale Horse" more effectively, and he would have had no compeer—Mr. Fuseli; whose compositions are of a higher order than those of any other in this country, and will be duly estimated when the price set upon his works cannot be useful to their author. No one is valued till he is dead; after the last sigh has sobbed from the body comes the time for some to suspect that they had inflicted pangs upon its infirmity when living, and a desire to know more of a man, the rufflings of whose dying pillow the breath of their friendship might have smoothed, and whom, to the extent of their comprehension they might have known, if their little feelings, in a state too easy, had not excluded him from their society.
FLORAL DIRECTORY.
Upright Chickweed. Veronica triphyllos.
Dedicated to St. Droctavœus.